The Panama Canal is a crucial global trade route, linking the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and facilitating the movement of goods between major economic hubs. In recent years, China has expanded its investments in ports and infrastructure surrounding the canal, sparking concerns about its growing influence. The United States, a key stakeholder in the canal’s operations, has voiced security worries over Chinese involvement.
This article explores China’s presence around the Panama Canal, its economic and geopolitical implications, and the potential consequences for international trade and security.
China’s Strategic Investments in Panama
China’s increasing involvement in Panama aligns with its global Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to strengthen infrastructure and trade networks worldwide. Since Panama joined the BRI in 2017, Chinese companies have significantly increased their footprint in the region.
Chinese-Controlled Ports Around the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal is surrounded by five major container ports, all operated by foreign companies. The two largest, Cristóbal and Balboa, are managed by a subsidiary of CK Hutchison Holdings, a Hong Kong-based corporation.
Although CK Hutchison is a private company, experts have expressed concerns about its potential ties to China’s Communist Party (CCP). Given China’s national security laws, Beijing could exert influence over Hong Kong-based firms during a conflict or crisis.
Infrastructure Projects Funded by Chinese Companies
Beyond port operations, Chinese firms are deeply involved in Panama’s infrastructure, financing and building key projects:
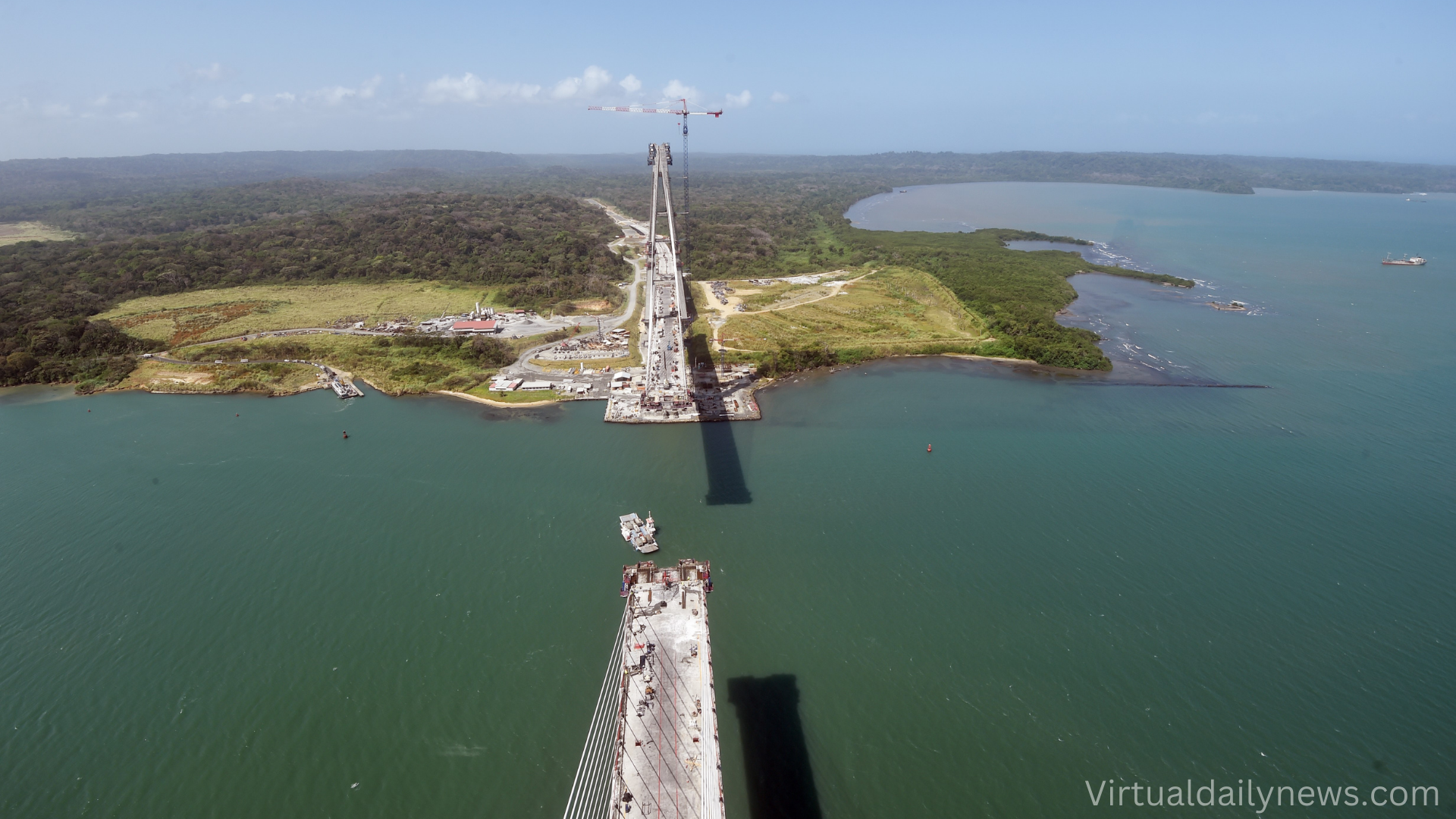
Fourth Bridge Over the Panama Canal
A $1.42 billion contract was awarded to a Chinese consortium for the Fourth Bridge project, connecting Panama City with West Panama. The bridge, which has faced construction delays, is a significant transportation project aimed at easing congestion.
Amador Cruise Terminal
Built by China Harbour Engineering Company, the Amador Cruise Terminal on the Pacific side of the canal enhances Panama’s tourism sector. The project allows the country to host larger cruise ships, boosting economic activity.
Panama City Metro Expansion
The China Railway Tunnel Group Company is developing an extension to the Panama City Metro, which will run beneath the canal’s southern entrance. This addition is expected to improve public transportation and connectivity in the region.
Geopolitical Implications of China’s Presence
China’s growing involvement in the Panama Canal region has raised concerns among U.S. policymakers. The U.S. remains the dominant investor and trade partner in Panama but fears that Chinese-controlled infrastructure could pose security risks.
U.S. Government’s Response
Washington has been closely monitoring China’s activities around the Panama Canal. Some U.S. officials worry that Chinese-controlled ports could be leveraged to restrict access for American military and commercial vessels during a geopolitical crisis.
In 2023, U.S. Southern Command General Laura J. Richardson warned lawmakers that China’s strategic presence in the region could be used to limit U.S. naval operations.
Panama’s Position on Chinese Investments
Despite concerns from the U.S., Panama maintains control over the canal through the Panama Canal Authority (ACP). Panamanian officials emphasize that while they welcome foreign investment, the country retains full sovereignty over the canal’s operations.
However, due to U.S. diplomatic pressure, Panama recently announced its decision to exit the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), signaling a potential policy shift away from Chinese-led projects.
Economic Impact of China’s Investments in Panama
China’s financial involvement in Panama has both positive and negative implications:
Positive Economic Contributions
- Job Creation: Infrastructure projects have provided employment opportunities for Panamanians.
- Improved Infrastructure: New bridges, ports, and metro expansions have modernized Panama’s transportation network.
- Trade Boost: Increased investments have strengthened Panama’s position as a global trade hub.
Potential Risks and Challenges
- Debt Dependency: Some analysts fear that Panama could become financially dependent on Chinese loans.
- Strategic Influence: The possibility of Chinese control over critical infrastructure remains a concern for global security.
- Project Cancellations: Several high-profile Chinese-led projects have been shelved or discontinued, casting doubts on long-term collaboration.
China’s Declining Influence in Panama?
Despite China’s initial investment surge, Panama has recently moved away from several Chinese-led projects:
- Proposed High-Speed Rail Project (Panama City to David) – Shelved after a change in government.
- Isla Margarita Port Development – Canceled in 2022.
- Chinese Embassy Project on Amador Causeway – Rejected in 2018 due to national security concerns.
According to Panamanian economist Eddie Tapiero, 50% of Chinese-funded projects initiated after 2017 have either been canceled or suspended.
Global Trade and Security Considerations
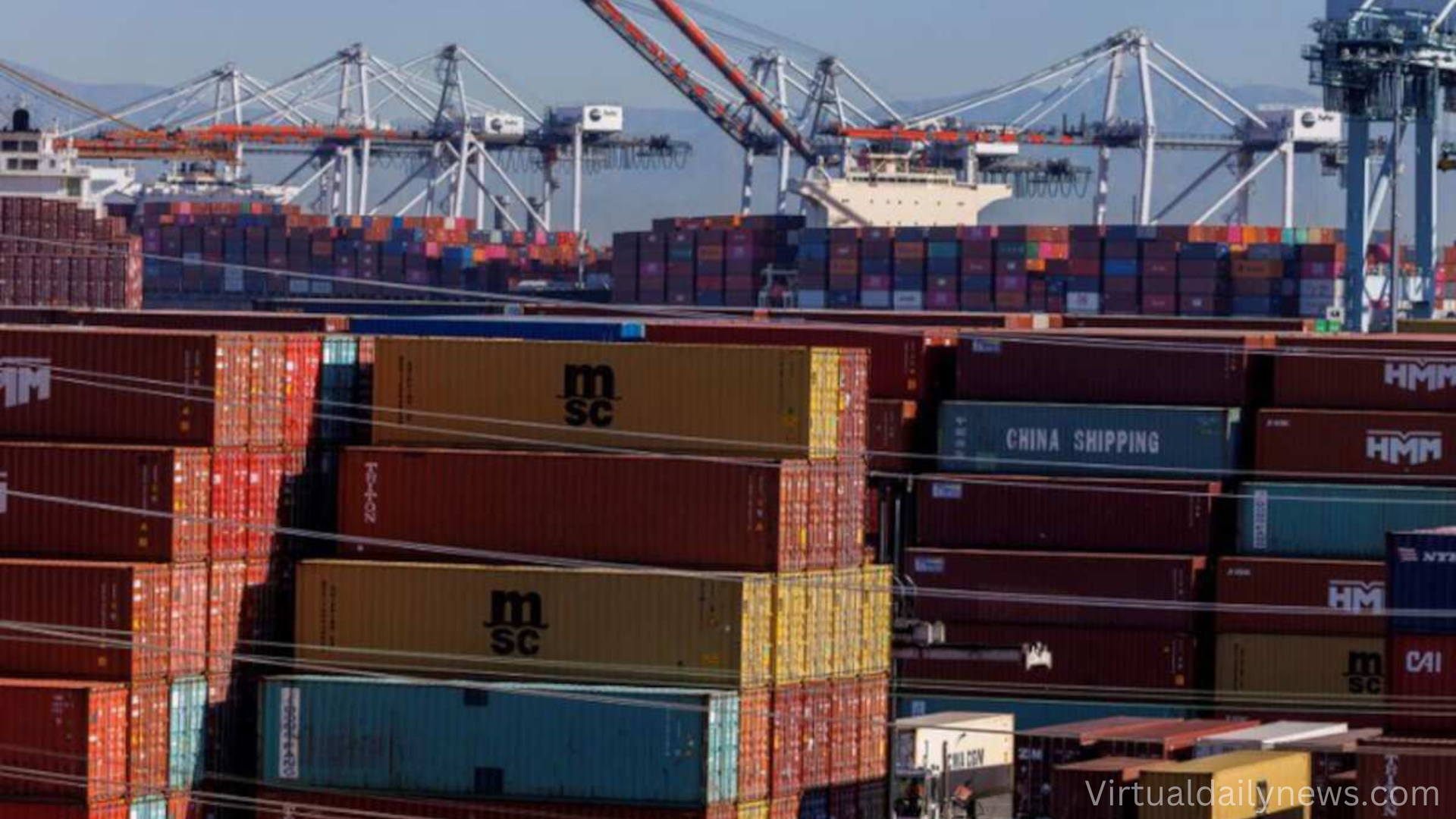

The Panama Canal remains crucial for international shipping, handling 21% of Chinese cargo shipments and a significant portion of U.S. maritime trade. While Chinese investments in surrounding infrastructure are growing, the U.S. remains the top user and investor in Panama.
Panama is likely to balance relationships between the U.S. and China, ensuring economic growth while safeguarding its strategic independence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does China own the Panama Canal?
No. The Panama Canal is owned and operated by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP). However, Chinese companies control key ports and infrastructure projects in the region.
Why is the U.S. concerned about China’s presence in Panama?
The U.S. fears that China’s control over ports and infrastructure near the canal could pose national security risks and impact global trade.
What are the leading Chinese investments in Panama?
China has invested in ports (Cristóbal and Balboa), bridges, cruise terminals, and metro expansions around the canal.
Has Panama benefited from Chinese investments?
Yes. Chinese investments have improved infrastructure and trade, but concerns over debt dependency and geopolitical influence remain.
What is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)?
The Belt and Road Initiative is China’s global strategy to invest in infrastructure and trade networks, including projects around the Panama Canal.
Why did Panama withdraw from the Belt and Road Initiative?
Panama left the BRI due to U.S. diplomatic pressure and concerns about Chinese-led projects failing to deliver expected benefits.
What role does the Panama Canal play in global trade?
The Panama Canal is a key trade route that reduces shipping time between Asia, the Americas, and Europe. It handles 14,000 ships annually.
Could China block the Panama Canal?
While China does not control the canal, concerns remain about its strategic influence over surrounding ports that could impact trade in a crisis.
Conclusion
China’s expanding footprint around the Panama Canal reflects its broader strategy to strengthen global trade routes. While Chinese investments have enhanced Panama’s infrastructure and trade sector, concerns over security, debt dependency, and geopolitical influence remain.
Despite the U.S. maintaining its dominance as the canal’s largest investor and trade partner, China’s involvement in Panama underscores the ongoing power struggle between global superpowers. As Panama navigates its foreign policy, it must carefully balance economic opportunities with national security considerations to secure its long-term interests.